Do I need Flat Food Surgery or treatment?
People with flat feet who do not experience pain or any other symptoms do not usually consult a doctor. Treatment is only required if there is pain in the foot or ankles. The doctor will diagnose the flat foot by examining the feet and observing the patient as they stand and walk. In some cases, they may order an X-ray or MRI scan.
What is a Flat Foot?
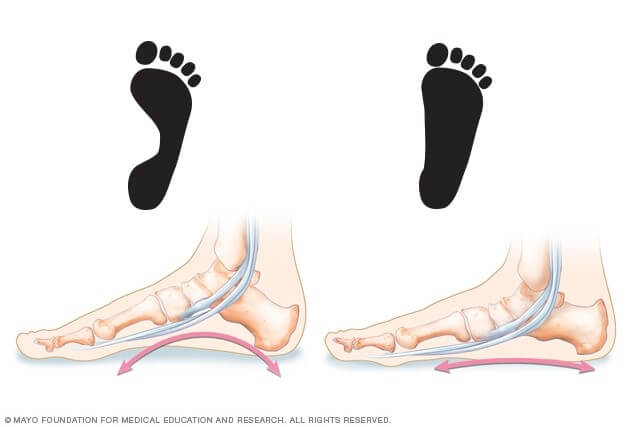
Flat foot, also called pes planus, is when the arch on the inside of the foot is flattened, and the entire sole of your foot touches the ground when you stand up. This is a common painless condition which can occur when arches are not developed during childhood. In other instances, flat foot may develop after an injury or even from the simple wear-and-tear of age.

How will having flat foot affect my overall health?
While having a flat foot might not sound like a big deal, it can contribute to problems in your ankles and knees an alteration in the alignment of your legs. The arch provides a spring to the step and helps distribute your body weight across your feet and legs. Without the arch, your foot may roll to the inner side when you are standing and walking. This is known as overpronation and may cause the foot to point outwards. This results in an abnormal strain and pressure acting not only onto your feet, but also on your ankles, knees, hips and back, which leads to a variety symptoms including:
- Feet tired easily
- Painful achy feet (especially in area of the arches and heels)
- The inside bottoms of your feet become swollen
- Bunions
- Heel pain
- Hammertoe
- Back, knee, hip pain
- Shin splints
What treatments are available?
It is important to note that there is no blanket treatment. Treatment is focus on specific aspects of the foot that require modification or healing. Often the first line of treatment is non-surgical.
Specific exercises – Some people with flat feet also have a short Achilles tendon. Exercises to stretch this tendon may help.
Insoles or Orthotics – A structurally supportive shoe might be more comfortable than sandals or shoes with minimal support.
Surgery – For more serious cases, surgery is usually the last resort. The orthopaedic surgeon may create an arch in your feet, repair tendons, or fuse the bones or joints.